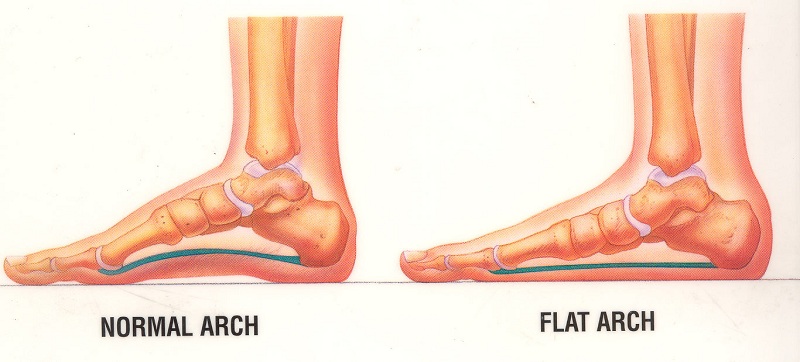
Flatfoot is a very common disease in the modern world, and it is not surprising if you started worrying about it soon after the birth of a baby. It should be understood that absolutely all newborn children have flat feet. The formation of regular bends of the leg occurs within a few years, sometimes it ends at 5-6 years of age and sometimes lasts up to 10-12 years. However, the children’s body does the greatest work on the formation of arches of the foot when the child learns to walk.
Proper formation of the anatomical arches of the foot is an important guarantee for the health of the entire spine. Its natural curves play the role of a kind of shock absorber, significantly reducing the load when walking, running, jumping, and any other movements in which the legs are involved.
But, as already noted, in a child, these curves are in the stage of appearance and strengthening. Only by the age of twelve can we say that the foot of the little patient is formed and draw conclusions about the presence of any pathology. Until then, a flatfoot in children is in principle, not quite the correct diagnosis – rather, we can talk about deviations from the average indicators of the development of the arches of the foot and the need for prevention.
The main signs of flatfoot
If it seems to you that the child has any problems with the legs, in no case should you treat them at home without consulting an orthopedic doctor? A signal to consult a doctor like this may be one or more of the following symptoms:
- Clubfoot. The parallel arrangement of the feet is considered the norm: this is how they are located if their muscles are strong enough and developed. Any deviations from the parallels can be regarded as violations.
- Pain in the feet and legs. When problems with the arches of the feet, these feelings are especially strong after physical exertion. If your child systematically complains of a similar problem – it is worth thinking seriously about the condition of his legs.
- Incorrect load distribution on the foot during walking. Most often it is about the fact that the baby is too hard on the inside of the foot. This feature is usually visible to the naked eye. It can be identified by the way the soles of the baby’s shoes are washed.
Prevention of flatfoot
For a child of preschool age, insufficiently formed arches of the foot are the norm. If you find the abnormalities mentioned above, or for any other reasons doubt the proper development of the legs of your baby, then you, as already mentioned, need to contact an orthopedist. Its recommendations should be strictly followed not only in the context of treatment but also as part of the prevention of the disease. Otherwise, you can harm the child.
So, for example, orthopedic shoes and orthopedic insoles, which firmly fix the leg of a small patient, are becoming increasingly popular. However, such products can be worn only according to medical indications and on the recommendation of a doctor. If you force a child with healthy legs to constantly walk in shoes with full rigid fixation, then the muscles of his feet will not work and, as a result, they will not develop. Therefore, do not try to correct such problems, based on your own ideas about flat feet and dubious advice from the Internet.
Below we will list the main measures for the prevention of flat-footedness, which will definitely not harm your child, but will only help prevent the development of the disease in the presence of its beginnings (and not serious deviations, for which you need to contact an orthopedist):
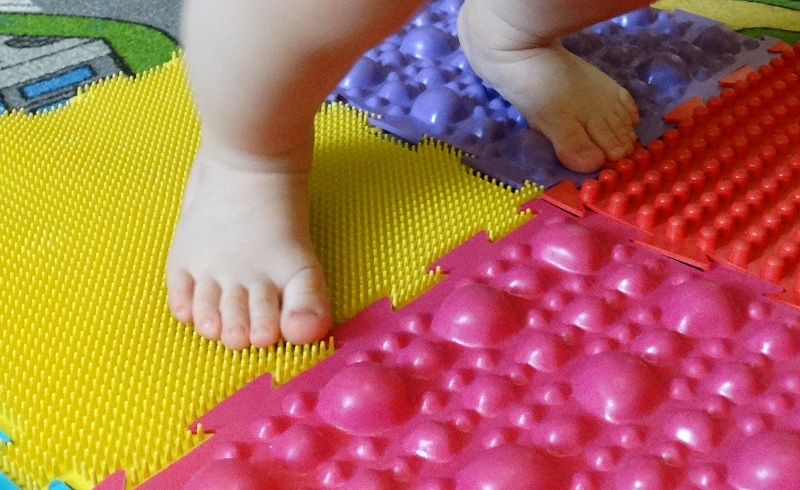
- Walking barefoot on an uneven surface. In fact, walking barefoot is the most natural and useful exercise for baby feet. It is this, in contrast to the wearing of stiff shoes that contributes to the active work and development of the muscles of the foot the formation of correct and durable arches. In order for the child to walk on an uneven surface, you can purchase a special mat or simply scatter something on the floor (small balls, nuts in the shell, etc.). And, of course, always let your little explorer run along the sand or grass when the opportunity presents itself.
- Choose the right shoes for your child. No need to buy products “butt”, as well as excessively free models. The stock size should be about 1 centimeter so that the instep shoes are located directly under the arch of the foot. It is advisable to buy shoes with a fairly dense and high heel (but not products with rigid fixation of the leg as a whole). And, of course, children are best to walk in shoes made from natural materials.
- Teach your child to perform preventive exercises. These can side steps on a gymnastic stick laid on the floor (the child must walk sideways so that the stick is located in the middle of the foot); walking on heels and socks, based on the inner and outer parts of the foot; rolls from heel to toe and back while standing. Such a simple gymnastics will not exactly harm the children’s legs, but, on the contrary, will contribute to their harmonious development.
- Watch for the child’s nutrition and so that he systematically receives feasible physical exertion, often walk with him in the fresh air, promptly treat any diseases. The general condition of the body, the activity of lifestyle always affects the development of all organs and systems, including the formation of arches of the feet.
Any more serious ways of dealing with potential flat-footedness for children are prescribed by an orthopedic surgeon.
What is flatfoot?
When it comes to a child over 12 years old and obvious pathologies in the development of his feet, we can talk about the following types of flatfoot:
- longitudinal;
- transverse;
- Combined;
In this case, we are talking about how the arch of the foot was not sufficiently formed. There is also a classification of flatfoot according to the degree of neglect:
- First degree This is a rather mild disease that is easy to cure and which is almost invisible to the naked eye.
- Second degree This is a more serious illness, which is often seen even by a non-specialist, is treated longer and more difficult, and also causes pain.
- Third degree If you follow your child, then this stage will not reach flat feet, but we still mention it. The third-degree entails severe pain, severe deformity of the feet, gait distortion, and is intractable.
Flatfoot is also divided into congenital and acquired. The first happens only in 3% of all people, however, and this is a sufficient percentage to, again, periodically show your child to an orthopedist. Acquired flat feet may appear due to the following main reasons:
- Rahita In other words, disorders of the vitamin and mineral metabolism in the body of a small patient often lead to deformation or underdevelopment of the arches of the feet.
- Cerebral palsy. Such flatfoot is also called paralytic.
- Suffered injuries. If a child has injured legs or feet, the muscles of the latter may well be incorrect or not sufficiently developed.
- Weak muscle tone of the foot. Most often, a similar reason is detected in children leading a low-active lifestyle, as well as in those patients who, since childhood, have been walking in a rigidly fixing foot.
Treatment of flatfoot
If you find your child has any of the symptoms listed at the beginning of this article, and ask yourself “What to do?”, then the answer is one: take him to an orthopedic surgeon. In principle, even without the detection of such symptoms, it would not be superfluous to visit such a doctor once every few months (in the first year of life) and once every six months or a year (in the next years of life). When a child reaches the age of 12, the problem becomes especially urgent, since in this case, it is already possible to speak of a serious, “adult” flatfoot.
The treatment, again, is prescribed by the doctor for each individual patient individually. It may include the following methods:
- The course of physiotherapy. It is about performing a number of procedures both within the walls of a medical institution and at home.
- Wearing special corrective shoes, best of all – with orthopedic insoles, made on the patient’s casts.
- Performing reflexology and special foot and foot massage.
- Visiting a physical therapy room and regularly performing a number of specific exercises.
- Wearing plaster cast and langet (resort to this measure only in very serious cases).
- Surgery (this measure is also applied in case of a deep and neglected disease).
Thus, even the existing flatfoot is quite realistic to cure, if it was detected in a timely manner. However, in most cases, it is possible to prevent the development of the disease altogether if simple preventive measures are taken from early childhood. Anyway, if any pathologies are found, one should contact an orthopedic surgeon, and subsequently – follow all his advice. Take care of the health of your baby’s feet – and he will enter adulthood without flat feet!